Continuous glucose monitoring systems provide accurate and continuous feedback on your glucose levels, helping you to manage your diabetes effectively. Get real-time insights and take control of your health with our reliable monitoring technology.
Diabetes is a chronic disease that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a condition where the body either does not produce enough insulin or does not use it effectively, resulting in high blood sugar levels. Proper management of diabetes is crucial in preventing complications, such as heart disease, kidney disease, and vision loss. One vital aspect of diabetes management is monitoring blood sugar levels regularly. In recent years, continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) have emerged as a game-changer in the world of diabetes care.
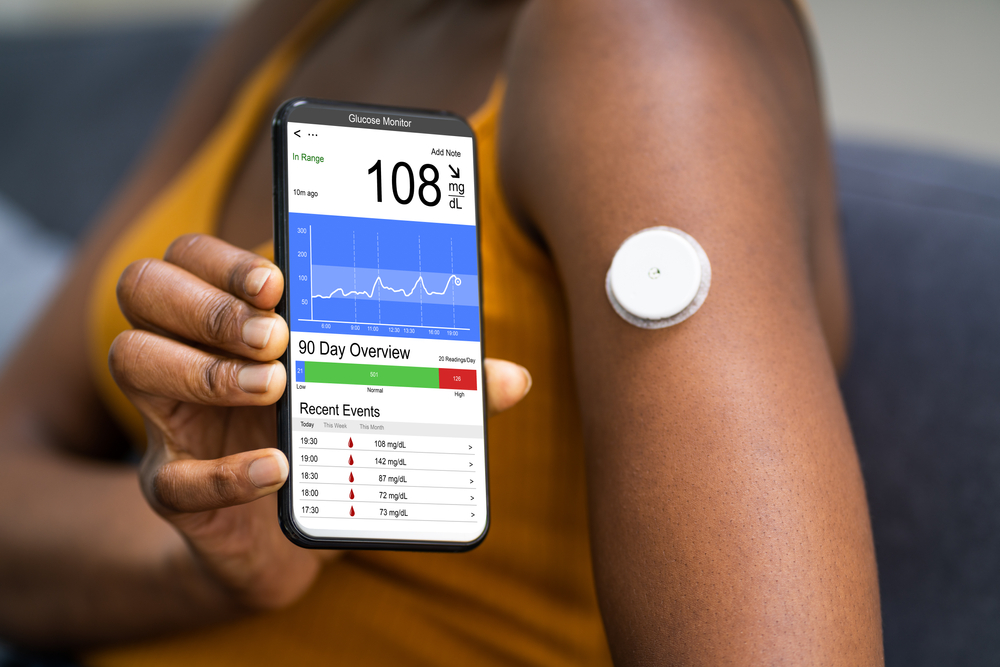
What is a Continuous Glucose Monitor?
A continuous glucose monitor is a small medical device that measures glucose levels in the interstitial fluid (the fluid surrounding the body's cells) throughout the day and night. The device typically consists of three parts: a sensor, a transmitter, and a receiver. The sensor is inserted under the skin, usually on the abdomen or upper arm, and measures glucose levels every few minutes. The transmitter, attached to the sensor, wirelessly sends this data to the receiver, which can be a standalone device or a compatible smartphone or smartwatch.
CGMs provide real-time glucose readings, allowing users to see their current glucose level and trends over time. Some advanced models also include alerts to warn users when their glucose levels are too high or too low, helping them make timely adjustments to their treatment plan.
Who Needs a Continuous Glucose Monitor?
Continuous glucose monitors are primarily designed for people with diabetes, particularly those with type 1 diabetes or insulin-dependent type 2 diabetes. However, they can also be beneficial for individuals with other conditions that require close monitoring of blood sugar levels, such as gestational diabetes or cystic fibrosis-related diabetes.
CGMs are particularly useful for those who experience frequent episodes of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) or have difficulty recognizing the symptoms of low blood sugar. They can also help people who struggle to maintain stable blood sugar levels or have a high level of glucose variability.
It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine if a CGM is the right choice for your specific situation. Your doctor will consider factors such as your age, duration of diabetes, frequency of blood sugar testing, and history of severe hypoglycemia before recommending a CGM.
Benefits of Continuous Glucose Monitoring Devices
Continuous glucose monitoring devices offer several benefits compared to traditional blood glucose testing methods, such as fingerstick tests. Some of these advantages include:
-
More accurate and comprehensive data: CGMs provide real-time glucose readings and trends, allowing users to make better-informed decisions about their diabetes management. This additional data can help identify patterns, such as nocturnal hypoglycemia or post-meal hyperglycemia, that may not be detected by fingerstick testing alone.
-
Improved glycemic control: Studies have shown that CGM users experience improved glycemic control, as measured by a reduction in their average blood sugar levels (HbA1c). This improved control can lower the risk of diabetes-related complications, such as kidney disease or retinopathy.
-
Enhanced quality of life: Many CGM users report enhanced quality of life, as they can make more informed decisions about their diabetes management and avoid severe hypoglycemia episodes. Additionally, the reduced need for fingerstick testing can lead to less pain and inconvenience.
-
Better decision-making: With the continuous data provided by CGMs, users can make more informed decisions about their insulin dosages, food choices, and physical activity levels. This can lead to more stable blood sugar levels and improved overall health.
Cost
The cost of continuous glucose monitoring devices can vary depending on the specific model and features. CGMs are usually more expensive than traditional blood glucose meters, with the price of the device ranging from $1,000 to $3,000. Sensor replacements, which are needed every 7 to 14 days, can cost an additional $300 to $500 per month. However, it is important to consider the potential long-term savings associated with improved glycemic control, such as reduced healthcare costs and a lower risk of complications.
Many insurance companies and government healthcare programs, such as Medicare, cover the cost of CGMs for qualifying individuals. It is essential to check with your insurance provider to determine your coverage and any out-of-pocket expenses.
Special Offer: 20% Off Available
If you are considering a continuous glucose monitoring device, now is a great time to take advantage of a special offer. Currently, there is a 20% off promotion available for those interested in obtaining a CGM. This discount can significantly reduce the initial cost of the device, making it more accessible for those in need.
Continuous glucose monitors have revolutionized diabetes management, providing users with accurate and comprehensive data to make informed decisions about their treatment plan. CGMs can help improve glycemic control, reduce the risk of complications, and enhance the quality of life for people with diabetes. With the current 20% off promotion available, it is an excellent opportunity for those considering a CGM to take advantage of the many benefits these devices offer. Consult with your healthcare professional to determine if a continuous glucose monitoring device is the right choice for you.